Answer:
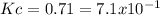
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since the equilibrium constant is written including gaseous and aqueous species only, for this reaction, it is:
![Kc=[O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/dsifcjmk9i3f32mvblowgl7v593ljxlw1u.png)
Thus, since the volume is missing, we are going to assume 1 L, but you can change it based on the one you are given, thus, the concentration of oxygen at equilibrium is:
![[O_2]=(22.7g*(1mol)/(32g) )/(1L) =0.709M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mh6y47gulsbv23qacqzysh0eub03zogt1g.png)
It means, that the equilibrium constant, with two significant figures is:
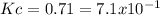
Best regards.