Answer:
F = -kmv
Step-by-step explanation:
The computation is shown below:
As we know that
a = acceleration
v = velocity
Given that
v = v_i - kx
Based on the above information
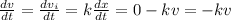
a = -kv ..................(i)
Now multiply both sides of an equation
BY mass of the object
ma = -kmv
F = -kmv
So if there is no other external forces so the force is on object i.e.
F = -kmv