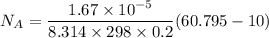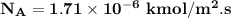Answer:
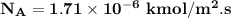
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
The total length = 0.20 m
Diameter = 0.01 m
Temperature = 298 K
Pressure = 101.32 kPa
The partial pressure of CO2 i.e
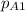 is 456 mm Hg at one end
is 456 mm Hg at one end
To kPa, we have:
=
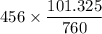
= 60.795 kPa
The partial pressure of CO2 i.e.
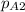 at the other end is 76 mm Hg
at the other end is 76 mm Hg
To kPa; we have
=
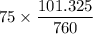
= 9.999 kPa
 10 kPa
10 kPa
The diffusion coefficient of CO
 in N
in N
 is 1.67 × 10⁻⁵
is 1.67 × 10⁻⁵
Universal gas constant = 8.314 J/mol/k
For equimolar counter-diffusion between the CO2 and N2 gases, the molar flux of CO
 can be estimated by using the formula:
can be estimated by using the formula:
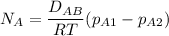
replacing our values from the above parameters then: