Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the information given :
we can understand the solute is glucose and the solvent is water,
So, the weight of glucose = 20.23 g
the molecular weight of glucose = 180.2 g/mol
weight of water = 95. 75 g
the molecular weight of water = 18.02 g/mol
pure vapor pressure of water
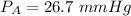 at 27°C
at 27°C
moles of glucose = weight of glucose/ molecular weight of glucose
= 20.23/180.2
= 0.11 mole
moles of water = weight of water / molecular weight of water
= 95.75/18.02
= 5.31 mole
mole fraction of glucose
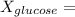 (moles of glucose)/(moles of glucose+ moles of water)
(moles of glucose)/(moles of glucose+ moles of water)
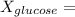 0.11/(0.11 + 5.31)
0.11/(0.11 + 5.31)
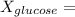 0.0203
0.0203
mole fraction of glucose
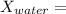 (moles of water)/(moles of water+ moles of glucose)
(moles of water)/(moles of water+ moles of glucose)
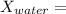 5.31/ (5.31 + 0.11)
5.31/ (5.31 + 0.11)
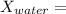 0.9797
0.9797
Using Raoult's Law:
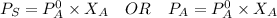
where:
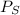 = vapor pressure of the solution
= vapor pressure of the solution
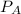 = total vapor pressure of the solution
= total vapor pressure of the solution
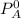 = vapor pressure of the solvent in the pure state
= vapor pressure of the solvent in the pure state
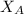 = mole fraction of solvent i.e. water
= mole fraction of solvent i.e. water
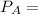 95.75 × 0.9797
95.75 × 0.9797
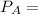 93.81 mmHg
93.81 mmHg
the total vapor pressure of the solution = 93.81 mmHg