Answer:
The initial speed of the water droplets is approximately 14.904 meters per second.
Step-by-step explanation:
We can describe the water jet from archerfish as part of parabolic motion, which consists of the superposition of two different motions. First, an horizontal motion at constant velocity and, second, a free fall motion. The maximum height is reached when vertical component of speed is zero. The equation of motion is described below:
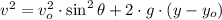
Where:
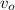 - Initial speed of the water jet, measured in meters per second.
- Initial speed of the water jet, measured in meters per second.
 - Current speed of the water jet, measured in meters per second.
- Current speed of the water jet, measured in meters per second.
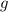 - Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
- Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
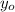 - Initial height, measured in meters.
- Initial height, measured in meters.
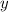 - Current height, measured in meters.
- Current height, measured in meters.
Now we clear the initial speed within equation:
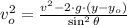
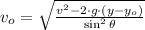
If we know that
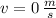 ,
,
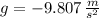 ,
,
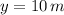 ,
,
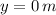 and
and
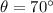 , the initial speed of the water droplets is:
, the initial speed of the water droplets is:
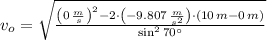
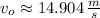
The initial speed of the water droplets is approximately 14.904 meters per second.