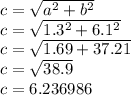Answer:
Explanation:
First things first, let's explain what a right triangle is. The definition is very simple and might even seem obvious for those who already know it: a right-angled triangle is a triangle where one and only one of the angles is exactly 90°. The other two angles will clearly be smaller than the right angle because the sum of all angles in a triangle is always 180°. In a right angled triangle the sides are defined in a special way. The side opposing the right angle is always the biggest in the triangle and receives the name of "hypotenuse". The other two sides are called catheti. The hypotenuse is opposite the right angle and can be solved by using the Pythagorean theorem. In a right triangle with cathetus a and b and with hypotenuse c, Pythagoras' theorem states that: a² + b² = c².
To solve for c, take the square root of both sides to get c = √(b²+a²). This extension of the Pythagorean theorem can be considered as a "hypotenuse formula".
Steps to solve: