Answer:
1. Velocity = 75.39 m/s
2. Air resistance
3. Mass of the coin
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Given that the height of the building is 290 m. From Newton's third law of motion,
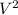 =
=
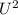 + 2gh
+ 2gh
where: V is the final velocity of the coin, U is the initial velocity, g is the force of gravity and h is the height.
Since the coin was dropped from a height, its initial velocity is zero. The force of gravity is taken as 9.8 m/
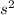 , so that:
, so that:
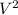 = 0 + 2 x 9.8 x 290
= 0 + 2 x 9.8 x 290
= 5684
V =
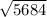
= 75.3923
The velocity with which the coin hits the ground is 75.39 m/s.
2. Air resistance: During the free fall of the coin, the direction of wind flow could either cause an increase or decrease the value predicted.
ii. Mass of the coin: This can also affect the predicted value.