Answer:
74.0 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
In the equivalence point we have:
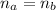
Where:
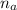 is the number of moles of the acid
is the number of moles of the acid
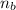 is the number of moles of the base
is the number of moles of the base
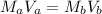
Where M is the concentration and V is the volume
Hence the volume of the base is:
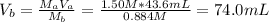
Therefore, is needed 74.0 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to reach the equivalence point.
I hope it helps you!