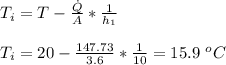Answer:
The answer is below
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
kg (glass) = 0.78 W/m⋅K, ka (air) = 0.026 W/m⋅K, h1 = 10 W/m2⋅K, h2 = 25 W/m2⋅K, glass length = Lg = 3 mm = 0.003 m, Lo = 3 mm = 0.003 m, La = 12 mm = 0.012 Height = 1.5 m, width = 2.4 m, room temperature = T = 20°C. Therefore:
Total resistance per unit area is given as:
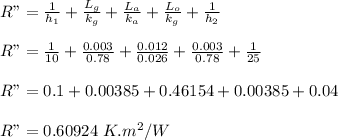
Area = A = height * width = 1.5 m × 2.4 m = 3.6 m²
The change in temperature = ΔT = 20 °C - (-5 °C) = 25 °C
The rate of heat loss is given as:
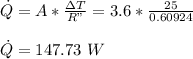
The inner surface temperature (Ti) is given as: