Answer:
The voltage drop across the wire is 2 V
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
length of wire, L = 10 m
current density, I/A, μ = 4 x 10⁶ (A/m²)
wire conductivity, σ = 2 x 10⁷ (S/m)
The resistivity of wire is given by;
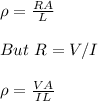
Conductivity, σ = ¹/ρ
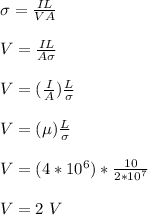
Therefore, the voltage drop across the wire is 2 V