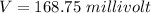Answer:
The value is
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The workdone is
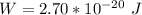
Generally charge on the positive sodium ion is equivalent to the charge on a proton, the value is

Generally the potential difference between the inner and outer surfaces of the cell is mathematically represented as
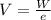
=>
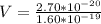
=>
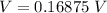
converting to millivolt
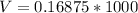
=>