Answer:
cyclohexane.
Step-by-step explanation:
Alkanes are saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons. They form homologous series with the general molecular formula
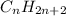 , where n is a whole number which is equal to or greater than 1. The first member of the series is
, where n is a whole number which is equal to or greater than 1. The first member of the series is
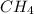 . Alkanes are tetrahedral in shape. All alkanes have similar names with the suffixes -ane. The physical properties such as melting and boiling point, density and states of matter of alkanes increases steadily with increasing molar mass. They undergo substitutional and combustion reactions;.
. Alkanes are tetrahedral in shape. All alkanes have similar names with the suffixes -ane. The physical properties such as melting and boiling point, density and states of matter of alkanes increases steadily with increasing molar mass. They undergo substitutional and combustion reactions;.
For secondary hydrocarbon, they exist in a ring shape or have a double functional group attached to the structure of the organic compound.
Here, an alkane with 6 carbon atoms is known as hexane but when it exists in ring shape then it is called cyclohexane.
The structure can be found in the attached file below.