Answer:
H₃O⁺.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, ionization of ethanol yields hydrogen cations and ethoxide anions as follows:
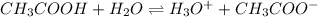
Which is at equilibrium as ethanol is a weak acid. Thus, since the conjugate acid is formed by the outgoing H⁺ and the water, we say that the conjugate acid is then the hydroxonium ion, H₃O⁺ whereas the conjugate base is the remaining anion CH₃COO⁻.
Best regards.