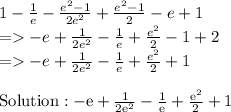Answer:
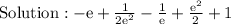
Explanation:
Your set up for the 'area of the shaded region' is absolutely correct. But when it comes to evaluating them, you are slightly off.
If we break this expression into parts, we have (eˣ - 2e²ˣ)dx on the interval [- 1 to 0] and (e²ˣ - eˣ)dx on the interval [0 to 1]:
(eˣ - 2e²ˣ)dx on the interval [- 1 to 0],
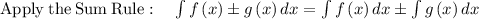
=> eˣdx - e²ˣdx on the interval [- 1 to 0]
=>
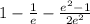
(e²ˣ - eˣ)dx on the interval [0 to 1],
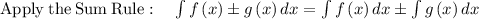
=> e²ˣdx - eˣdx on the interval [0 to 1],
=>
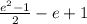
And now if we add the remaining fractions as expected, we will receive our answer. The set up would be as follows: