Answer:
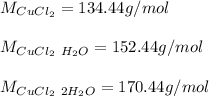
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since anhydrous copper (II) chloride is CuCl₂ whose molar mass is:
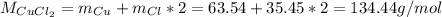
We can also find copper (II) chloride both monohydrate and dihydrate as CuCl₂·H₂O and CuCl₂·2H₂O respectively, whose molar masses are:
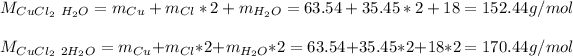
Best regards.