Answer: W =
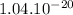 J
J
Step-by-step explanation: Since the potassium ion is at the outside membrane of a cell and the potential here is lower than the potential inside the cell, the transport will need work to happen.
The work to transport an ion from a lower potential side to a higher potential side is calculated by
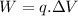
q is charge;
ΔV is the potential difference;
Potassium ion has +1 charge, which means:
p =
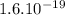 C
C
To determine work in joules, potential has to be in Volts, so:
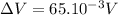
Then, work is
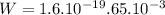
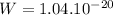
To move a potassium ion from the exterior to the interior of the cell, it is required
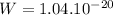 J of energy.
J of energy.