Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information, we are to compare the minimum energies required to remove a neutron from
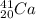 ,
,
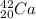 and
and
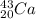
To start with
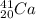 ; the minimum energy required to remove a neutron from
; the minimum energy required to remove a neutron from
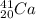 is :
is :
=
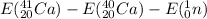
= (38156.36 - 37225.15 -939.57) MeV
= -8.36 MeV Since energy is being given out
Thus, E = 8.36 MeV
the minimum energy required to remove a neutron from
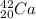 is :
is :
=
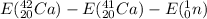
= ( 39084.46 - 38156.36 - 939.57) MeV
= -11.47 MeV Since energy is being given out
Thus, E = 11.47 MeV
the minimum energy required to remove a neutron from
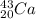 is :
is :
=
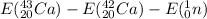
= (40016.10 -39084.46 -939.57) MeV
= - 7.93 MeV Since energy is being given out
Thus, E =7.93 MeV
Why there is a distinct increase of this energy for
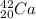 ?
?
This is as a result of electronic configuration of
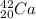 which posses the same number of proton and neutron, as such,
which posses the same number of proton and neutron, as such,
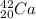 tends to acquire more stability. For this reason, it will be difficult to remove a neutron from
tends to acquire more stability. For this reason, it will be difficult to remove a neutron from
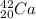 .
.