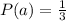Answer:
1
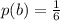
2
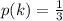
3
Explanation:
Generally when two fair 6-sided dice is rolled the doubles are
(1 1) , ( 2 2) , (3 3) , (4 4) , ( 5 5 ), (6 6)
The total outcome of doubles is N = 6
The total outcome of the rolling the two fair 6-sided dice is
n = 36
Generally the probability that doubles (i.e., having an equal number on the two dice) were rolled is mathematically evaluated as
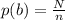
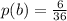
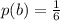
Generally when two fair 6-sided dice is rolled the outcome whose sum is 4 or less is
(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 1), (2, 2), (3, 1)
Looking at this outcome we see that there are two doubles present
So
The conditional probability that doubles were rolled is mathematically represented as
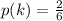
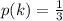
Generally when two fair 6-sided dice is rolled the number of outcomes that would land on different numbers is L = 30
And the number of outcomes that at least one die is a 1 is W = 10
So
The conditional probability that at least one die is a 1 is mathematically represented as
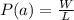
=>
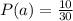
=>