Answer:
(a)
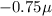 Coulomb
Coulomb
(b)
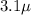 Coulomb
Coulomb
Step-by-step explanation:
Let
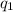 be the positive charge, in Coulumb, on the one sphere and
be the positive charge, in Coulumb, on the one sphere and
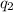 be the negative charge, in Coulumb, on the other sphere, where
be the negative charge, in Coulumb, on the other sphere, where
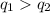 .
.
The center-to-center distance between the spheres is,
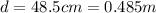 .
.
From Coulomb's law, the magnitude of the force,
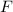 , between two point charges having magnitudes
, between two point charges having magnitudes
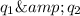 , separated by distance,
, separated by distance,
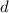 , is
, is
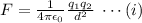
where,
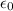 is the permittivity of free space and
is the permittivity of free space and
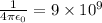 in SI units.
in SI units.
So, using equation (i), the attractive force between both the spheres is
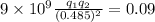
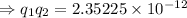
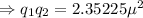 [as
[as
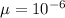 ]
]
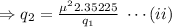
When both the sphere is connected by a thin conducting wire, then redistribution of charge take place and net charge , on combining both the spheres, is
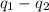 ( as
( as
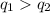 ).
).
Finally, the charge density on both the sphere will be the same.
Given that, both the sphere are identical, so, the quantity of charges on of charged on both the conducting spheres, after removing the conduction wire, will be the same.
So, the net charge on the individual sphere is
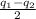 which is positive in nature.
which is positive in nature.
From equation (i), the repulsive force between the spheres is
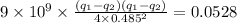
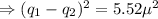 [ as
[ as
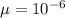 ]
]
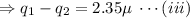
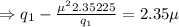 [using equation (ii)]
[using equation (ii)]
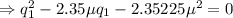
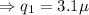 or
or
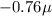
Taking positive sign as
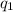 is the magnitude of charge.
is the magnitude of charge.
So, for
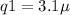
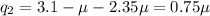 [from equation (iii)]
[from equation (iii)]
Hence,
(a) Negative charge on one of the spheres is,
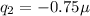 Coulomb.
Coulomb.
(b) Positive charge on the other sphere is,
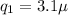 Coulomb.
Coulomb.