Answer:
Kp = 0.022
Step-by-step explanation:
Full question: ...With 2.3 atm of ammonia gas at 32. °C. He then raises the temperature, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of hydrogen gas to be 0.69 atm.
The equilibrium of ammonia occurs as follows:
2NH₃(g) ⇄ N₂(g) + 3H₂(g)
Where Kp is defined as:
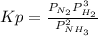
Where P represents partial pressure of each gas.
As initial pressure of ammonia is 2.3atm, its equilibrium concentration will be:
P(NH₃) = 2.3atm - 2X
Where X represents reaction coordinate
Thus, pressure of hydrogen and nitrogen is:
P(N₂) = X
P(H₂) = 3X.
As partial pressure of hydrogen is 0.69atm:
3X = 0.69
X = 0.23atm:
P(NH₃) = 2.3atm - 2(0.23atm) = 1.84atm
P(N₂) = 0.23atm
P(H₂) = 0.69atm
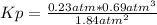
Kp = 0.022