Answer:
Written in Python:
def is_rightangled(a,b,c):
if abs(c**2 - (a**2 + b**2) < 0.001):
return "True"
else:
return "False"
a = float(input("Side 1: "))
b = float(input("Side 2: "))
c = float(input("Side 3: "))
print(is_rightangled(a,b,c))
Step-by-step explanation:
The function is defined here
def is_rightangled(a,b,c):
The following if statement implements Pythagoras theorem
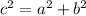 by checking if the left hand side is approximately equal to the right hand side
by checking if the left hand side is approximately equal to the right hand side
if abs(c**2 - (a**2 + b**2) < 0.001):
return "True"
else:
return "False"
If the specified condition is met, the if function returns true; Otherwise, it returns false.
The main function starts here
The next three line prompts user for the sides of the triangle
a = float(input("Side 1: "))
b = float(input("Side 2: "))
c = float(input("Side 3: "))
The next line calls the defined function
print(is_rightangled(a,b,c))