Answer:
I = 0.0931 A/cm^2 or 93.1 mA/cm^2
Step-by-step explanation:
The computation of the corresponding corrosion is shown below:
As we know that
The mathematical form is
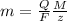
where,
m = substance mass
Q= total electric charge
F= Faradays constant i.e. = 96,500 C/mol
M = Substance molar mass
z = number of electrons transferred
Now
Q = It
where
I = current
And t = time
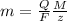
So,
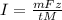
Now it is mentioned that
z=3, M=26.98 g/mol, m=0.25 g/cm2
So,
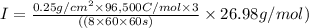
Hence,
I = 0.0931 A/cm^2 or 93.1 mA/cm^2