Answer:
The mole fraction of hexane is 0.61
Step-by-step explanation:
Raoult's law allows calculating the vapor pressure of a substance when it is forming part of an ideal solution, knowing its vapor pressure when it is pure (at the same temperature) and the composition of the ideal solution in terms of mole fraction.
Pi=xi*Pi°
where Pi is the partial pressure of component i in the solution, Pi ° is the vapor pressure of component i pure and xi is the mole fraction of component i in the liquid phase.
In a solution, once the components have reached chemical equilibrium, the total vapor pressure is:
Psolution=P1 + P2=x1*P1° +x2*P2°
In this case:
Psolution= xpentane*Ppentane° +xhexane*Phexane°
Being:
- Psolution= 258 torr
- xpentane + xhexane=1 ⇒ xpentane= 1 - xhexane
- Ppentane°= 425 torr
- xhexane= ?
- Phexane°= 151 torr
and replacing:
258 torr= (1-xhexane)* 425 torr + xhexane* 151 torr
you get:
258 torr= 425 torr - 425 torr*xhexane + xhexane* 151 torr
258 torr - 425 torr= - 425 torr*xhexane + xhexane* 151 torr
-167 torr= -274 torr*xhexane
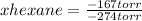
xhexane= 0.61
The mole fraction of hexane is 0.61