Answer: see proof below
Explanation:
Given: A + B + C = π → A + B = π - C
→ B + C = π - A
→ C + A = π - B
→ C = π - (B + C)
Use Sum to Product Identity: cos A + cos B = 2 cos [(A + B)/2] · cos [(A - B)/2]
Use the Sum/Difference Identity: cos (A - B) = cos A · cos B + sin A · sin B
Use the Double Angle Identity: sin 2A = 2 sin A · cos A
Use the Cofunction Identity: cos (π/2 - A) = sin A
Proof LHS → Middle:
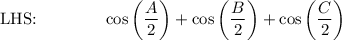
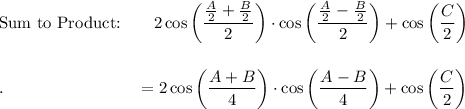
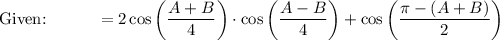
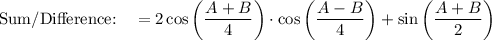

![\text{Factor:}\quad =2\cos \bigg((A+B)/(4)\bigg)\bigg[ \cos \bigg((A-B)/(4)\bigg)+\sin \bigg((A+B)/(4)\bigg)\bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/lmvee1xx0dbnrabxcn457a2r94hczbrobp.png)
![\text{Cofunction:}\quad =2\cos \bigg((A+B)/(4)\bigg)\bigg[ \cos \bigg((A-B)/(4)\bigg)+\cos \bigg((\pi)/(2)-(A+B)/(4)\bigg)\bigg]\\\\\\.\qquad \qquad \qquad =2\cos \bigg((A+B)/(4)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((A-B)/(4)\bigg)+\cos \bigg((2\pi-(A+B))/(4)\bigg)\bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/c1341ds6obt5cr3t1bh5qnsu2t0wqacn7g.png)
![\text{Sum to Product:}\ 2\cos \bigg((A+B)/(4)\bigg)\bigg[2 \cos \bigg((2\pi-2B)/(2\cdot 4)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((2A-2\pi)/(2\cdot 4)\bigg)\bigg]\\\\\\.\qquad \qquad \qquad =4\cos \bigg((A+B)/(4)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((\pi-B)/(4)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((\pi -A)/(4)\bigg)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/tb3h2na6j3zuphft1zuhx0ndjknywiwasz.png)
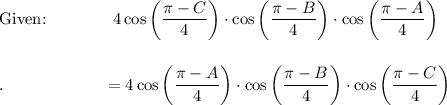
LHS = Middle
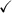
Proof Middle → RHS:
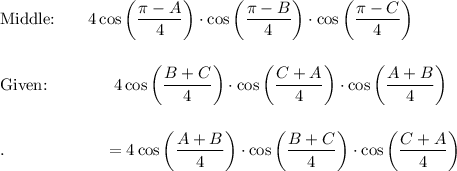
Middle = RHS