Answer:
The simplified expression for the fraction is
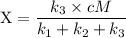
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
O3* → O3 (1) fluorescence
O + O2 (2) decomposition
O3* + M → O3 + M (3) deactivation
The rate of fluorescence = rate of constant (k₁) × Concentration of reactant (cO)
The rate of decomposition is = k₂ × cO
The rate of deactivation = k₃ × cO × cM
where cM is the concentration of the inert molecule
The fraction (X) of ozone molecules undergoing deactivation in terms of the rate constants can be expressed by using the formula:
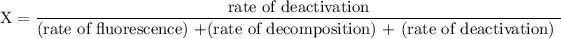
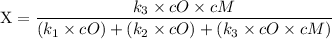
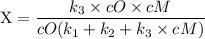
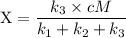 since cM is the concentration of the inert molecule
since cM is the concentration of the inert molecule