Answer:
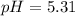
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, by considering the Henderson-Hasselbach equation:
![pH=pKa+log(([base])/([acid]) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8dmrsjloj30y2yhkiycsj9lw9h9a6w3h5m.png)
We can compute the pH before the addition of the NaOH:
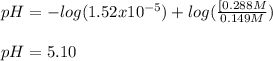
Nevertheless, if 0.061 moles of NaOH are added, we first need to compute the present moles of butanoic acid and sodium butanoate:
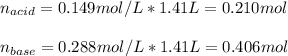
So the moles of acid and base after the addition are:
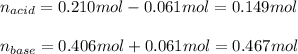
And the concentrations in the same volume:
![[acid]=(0.149mol)/(1.41L) =0.106M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vql0g1ehzwow9numz2mxhthncdqlt491i8.png)
![[base]=(0.467mol)/(1.41L) =0.331M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ol2chxdar3h1as5hew87j7f6xz96wazvpj.png)
Thus, the new pH is:
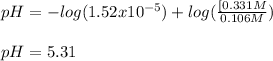
Which is a difference of pH of 0.21.
Best regards.