Answer:
The molarity is 0.22 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
The molarity of a solution can be calculated as follows:
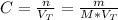
Where:
n: is the number of moles
V(T): is the total volume = 2000 mL = 2 L
M: is the molar mass = 36.46 g/mol
m: is the mass
The mass of HCl can be found using the following equation:
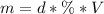
Where:
d: is the density = 1.19 g/mL
V: is the volume = 36.0 mL
% = 37.3 % by mass = 0.373
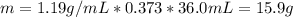
Hence, the molarity is:
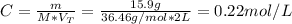
Therefore, the molarity is 0.22 M.
I hope it helps you!