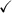Answer: see proof below
Explanation:
Given: A + B = C → A = C - B
→ B = C - A
Use the Double Angle Identity: cos 2A = 2 cos² A - 1
→ (cos 2A + 1)/2 = cos² A
Use Sum to Product Identity: cos A + cos B = 2 cos [(A + B)/2] · 2 cos [(A - B)/2]
Use Even/Odd Identity: cos (-A) = cos (A)
Proof LHS → RHS:
LHS: cos² A + cos² B + cos² C
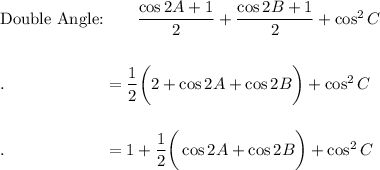
![\text{Sum to Product:}\quad 1+(1)/(2)\bigg[2\cos \bigg((2A+2B)/(2)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((2A-2B)/(2)\bigg)\bigg]+\cos^2 C\\\\\\.\qquad \qquad \qquad =1+\cos (A+B)\cdot \cos (A-B)+\cos^2 C](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/gbpts22xnyprmpangc06l2dh6z4fpat7l3.png)
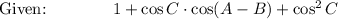
![\text{Factor:}\qquad \qquad 1+\cos C[\cos (A-B)+\cos C]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/e3g8aid2pq6xsrvzvblry83m6yc6qwzduq.png)
![\text{Sum to Product:}\quad 1+\cos C\bigg[2\cos \bigg((A-B+C)/(2)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((A-B-C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg]\\\\\\.\qquad \qquad \qquad =1+2\cos C\cdot \cos \bigg((A+(C-B))/(2)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((-B-(C-A))/(2)\bigg)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/osqixg5jk028we9g6o3uq5jfszifl4rzv0.png)
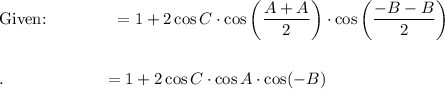
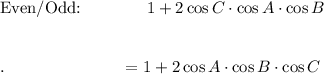
LHS = RHS: 1 + 2 cos A · cos B · cos C = 1 + 2 cos A · cos B · cos C