The question is missing some parts. Here is the complete question.
A technician compares repair costs for two types of microwave ovens (type I and type II). He believes that the repair cost for type I ovens is greater than the repair cost in type II ovens. A samplle of 61 type I ovens has a mean repair cost of $79.60, with a standard deviation of $23.47. A sample of 45 type II ovens has a mean repair cost of $75.25, with standar deviation of $15.07. Conduct a hypothesis test of the technician's claim at the 0.05 level of significance. Let
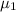 be the true mean repair cost for type I ovens and
be the true mean repair cost for type I ovens and
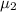 be the true mean repair cost for type II ovens.
be the true mean repair cost for type II ovens.
Step 1 of 4: State null and alternative hypothesis for the test.
Step 2 of 4: Compute the value of test statistics. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Step 3 of 4: Determine the decision rule for rejecting the null hypothesis. Round the numerical portion of your answer to 3 decimal places.
Step 4 of 4: Make the decision for the hypothesis test. (Reject or fail to reject Null Hypothesis)
Answer and Step-by-step explanation:
First, state null and alternative hypothesis:
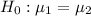
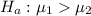
Use z-statistics:
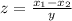
where x₁ and x₂ are the means and:
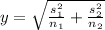
Calculating value of test stattistic:
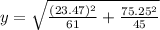
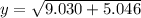
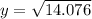
y = 3.752
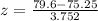
z = 1.16
The test statistics is z = 1.16
The decision rule for rejecting null hypothesis is:
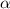 ≤ test statistics
≤ test statistics
Using z-score table, it is possible to determine p-value, which is:
p-value = 0.877
Comparing p-value with level of significance (α = 0.05):
0.877 > 0.05
Therefore, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.