Answer:
The percent elongation in the length of the specimen is 42%
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The gage length of the original test specimen
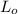 = 50 mm
= 50 mm
The final gage length
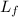 = 71 mm
= 71 mm
The area = 206 mm²
maximum load = 162,699 N
To determine the percent elongation in %, we use the formula:
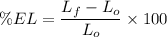
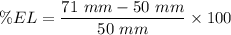
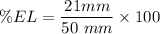
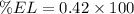
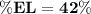
The percent elongation in the length of the specimen is 42%