Answer:
total work done = -5960.8 J
Step-by-step explanation:
given data
initial volume v1 = 0.22 m³
initial pressure p1 = 86 kPa
final pressue p2 = 101.3 kPa
solution
we apply here isothermal expansion that is express as
p1 × v1 = p2 × v2 ......................1
put here value
86 × 0.22 = 101.3 × v2
v2 = 0.1867 m³
and
work done will be here
w1 = p1 × v1 × ln(
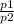 ) ....................2
) ....................2
w1 = 86 × 10³ × 0.22 ×
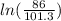
w1 = -3.097 × 10³ J
and
it is cooled to initial volume at constant pressure so here work done will be
w2 = p(v2 - v1) .................3
w2 = 86 × 10³ × ( 0.1867 - 0.22 )
w2 = -2863.8 J
so
total work done is
total work done = w1 + w2
total work done = -3097 + -2863.8
total work done = -5960.8 J