Answer:
Reaction:
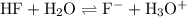 .
.
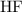 : Bronsted-Lowry Acid.
: Bronsted-Lowry Acid.
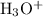 : Bronsted-Lowry conjugate Acid of
: Bronsted-Lowry conjugate Acid of
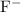 : Bronsted-Lowry conjugate Base of
: Bronsted-Lowry conjugate Base of
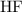 .
.
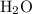 : Bronsted-Lowry Base.
: Bronsted-Lowry Base.
Step-by-step explanation:
In the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory, the acid in a reaction is the species that loses a proton,
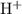 . The resultant species would be the conjugate base of that acid.
. The resultant species would be the conjugate base of that acid.
On the other hand, the Bronsted-Lowry base in a reaction is the species that accepts a proton
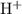 . The resultant species would be the conjugate acid of that base.
. The resultant species would be the conjugate acid of that base.
Identify the conjugate acid-base pairs in this reaction. Note that the two species in each pair are related by the gain or loss of a single proton. Therefore, their formula should look similar to each other.
For this reaction,
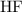 and
and
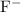 , as well as
, as well as
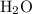 and
and
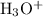 form two similar-looking reactant-product pairs:
form two similar-looking reactant-product pairs:
- The reactant
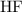 loses one proton to form the product
loses one proton to form the product
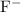 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
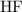 would be the Bronsted-Lowry acid, while
would be the Bronsted-Lowry acid, while
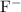 would be its conjugate base.
would be its conjugate base.
- The reactant
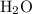 gains one proton to form the product
gains one proton to form the product
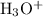 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
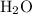 would be the Bronsted-Lowry base, while
would be the Bronsted-Lowry base, while
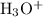 would be the conjugate acid.
would be the conjugate acid.