Answer:
![[OH^-]=9.24x10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/10pcl688sywp3j1kmb8hzg74magwi0sdm0.png) .
.
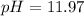 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since the ionization of methylamine is:
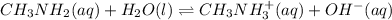
The equilibrium expression is:
![Kb=([CH_3NH_3^+][OH^-])/([CH_3NH_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cmpda3r8qs2evv0j8h2vh20suzm56k3en2.png)
And in terms of the reaction extent
 which is equal to the concentration of OH⁻ as well as that of CH₃NH₃⁺ via ice procedure we can write:
which is equal to the concentration of OH⁻ as well as that of CH₃NH₃⁺ via ice procedure we can write:
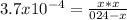
Whose solution for
 via quadratic equation is 9.24x10⁻³ M since the other solution is negative so it is avoided. Therefore, the concentration of OH⁻ is:
via quadratic equation is 9.24x10⁻³ M since the other solution is negative so it is avoided. Therefore, the concentration of OH⁻ is:
![[OH^-]=x=9.24x10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6qec673yagkfl7j13hl31k82qehmw4y593.png)
With which we can compute the pOH at first:
![pOH=-log([OH^-])=-log(9.24x10^(-3))=2.034](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/e21kfkejfcmeso3qv8ujzg34566moxmpzs.png)
Then, since pH and pOH are related via:
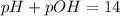
The pH turns out:
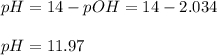
Best regards.