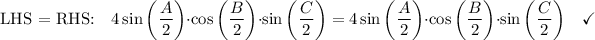Answer: see proof below
Explanation:
Given: A + B + C = π → A = π - (B + C)
→ B = π - (A + C)
→ C = π - (A + B)
Use Sum to Product Identity: sin A - sin B = 2 cos [(A + B)/2] · sin [(A - B)/2]
Use the following Cofunction Identity: cos (π/2 - A) = sin A
Proof LHS → RHS:
LHS: sin A - sin B + sin C
= (sin A - sin B) + sin C
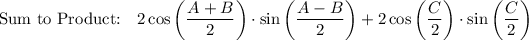
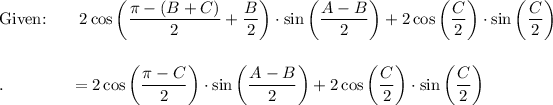
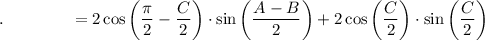
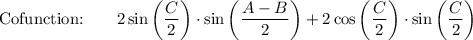
![\text{Factor:}\qquad 2\sin \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg[ \sin \bigg((A-B)/(2)\bigg)+\cos \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/cfeqm6epwesah8ghzhdv25o0hsfkq5avco.png)
![\text{Given:}\qquad 2\sin \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg[ \sin \bigg((A-B)/(2)\bigg)+\cos \bigg((\pi -(A+B))/(2)\bigg)\bigg]\\\\\\.\qquad \qquad =2\sin \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg[ \sin \bigg((A-B)/(2)\bigg)+\cos \bigg((\pi)/(2) -((A+B))/(2)\bigg)\bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9f3tmh9y5rp94oworh5q4ggdzbgaji0wuf.png)
![\text{Cofunction:}\qquad 2\sin \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg[ \sin \bigg((A-B)/(2)\bigg)+\sin \bigg((A+B)/(2)\bigg)\bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/oadcxxws65sltsws96bbl9svn7qkgcz8os.png)
![\text{Sum to Product:}\qquad 2\sin \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)\bigg[ 2\sin \bigg((A)/(2)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((B)/(2)\bigg)\bigg]\\\\\\.\qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad =4\sin \bigg((A)/(2)\bigg)\cdot \cos \bigg((B)/(2)\bigg)\cdot \sin \bigg((C)/(2)\bigg)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/mka9uf6u5kcgve9vy6ajl81vt4eie11p5z.png)