Answer:
10.95 or
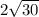
Explanation:
The Pythagorean Theorem is as follows:
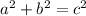
A and B represent the legs of the triangle, and C represents the hypotenuse.
For this problem, it gives us the legs. So, we have to find the hypotenuse.
Plug the values of the legs into the equation:
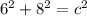
Now solve the equation to find the hypotenuse:
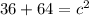 Distribute the squares
Distribute the squares
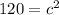 Add
Add
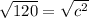 Square root both sides
Square root both sides
c = 10.95 or
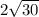
Therefore the length of the missing leg is 10.95 or
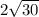 .
.
Hope this helps!! Ask questions if you need!