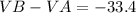Answer:
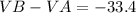
Step-by-step explanation:
Generally the workdone in moving the proton is mathematically represented as
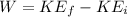
Where
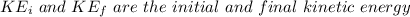
So
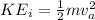
Here
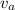 is the velocity at A with value 50 m/s
is the velocity at A with value 50 m/s
So

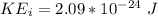
Also
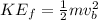
Here
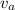 is the velocity at A with value
is the velocity at A with value
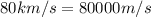
=>
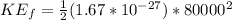
=>
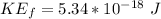
So
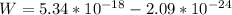

Now this workdone is also mathematically represented as
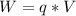
So
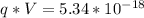
Here
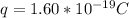
So
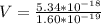
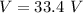
Generally proton movement is in the direction of the electric field it means that
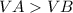
So