Answer:
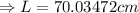
Step-by-step explanation:
For convenience, let's represent the thermal expansion coefficient by
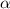 , i.e.
, i.e.
 .
.
Given that, for steel
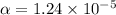 °
°
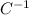 ,
,
initial length,
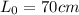 , initial temperature,
, initial temperature,
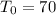 °
°
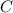 , and the final temperature,
, and the final temperature,
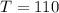 °
°
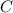 .
.
Let the length of the rod at
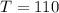 °
°
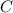 be
be
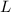 .
.
Now, change in length,
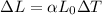
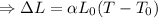
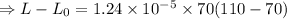
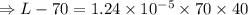
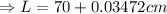
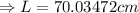
Hence, the length of the rod at
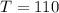 °
°
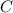 be
be
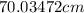 .
.