Answer:
The points are "(2,2)".
Explanation:
Given value:
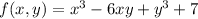
Finding the first partial derivation which is equal to 0.
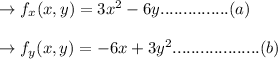
solve both the above equation by equal to 0.
For equation (a)
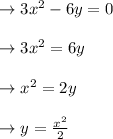
For equation (b)
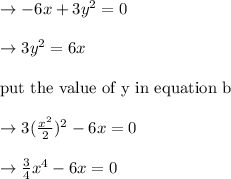
by solving the above value in the form of x we get:
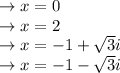
by solving the above value in the form of y we get:
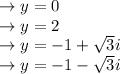
Solve the value by applying the second derivation method:
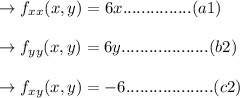
calculating the value of discriminate:
![d=f_(xx)(x,y) f_(yy)(x,y)-[f_(xy)(x,y)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/19je5b0dlh6bqt98tzdx7z0jsu0q8wnmdz.png)
The critical point of the given equation will be (2,2)
![d=f_(xx)(2,2) f_(yy)(2,2)-[f_(xy)(2,2)]^2\\\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/hhtbuktw3py1q9wud8ggjy9oixbcjmzb5i.png)
![= (6 * 2) (6 * 2) -[(-6)^2]\\\\= (12) (12) -[36]\\\\= 144 -36\\\\= 108\\\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/a0vlvk93qeqseqq4wiqtkouedhw4of9yzl.png)