Answer:
The velocity of the ejected electron from the ionized atom is 3.6 × 10⁵ m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the conservation of energy, we can write that
Photon energy (E) = Ionisation energy (I.E) + Kinetic energy (K.E)
Photon energy, E =
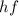
Where
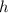 is Planck's constant (
is Planck's constant (
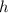 = 6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ kgm²/s)
= 6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ kgm²/s)
and
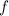 is the frequency
is the frequency
Also,
Kinetic energy, K.E =
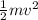
Where
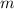 is mass
is mass
and
 is velocity
is velocity
Hence, we can write that
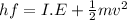
But,
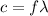
where
 is the speed of light (
is the speed of light (
 = 3.0 × 10⁸ m/s)
= 3.0 × 10⁸ m/s)
and λ is the wavelength
∴
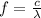
Then,
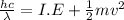
From the question, the first ionisation energy of sodium is 496 kJ/mol
This is the ionisation energy for 1 mole of sodium,
For 1 atom of sodium, we will divide by Avogadro's constant
∴ The ionisation energy becomes
(496 KJ/mol) / (6.02 × 10²³ molecules)
= 8.239 × 10⁻¹⁹ J
This is the ionisation energy for one atom of sodium
Now, to determine the velocity of the ejected electron from the ionized atom,
From,
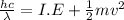
Then,
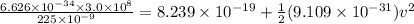
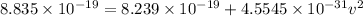
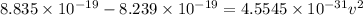
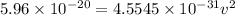
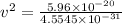
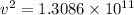
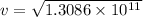
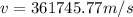
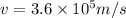
Hence, the velocity of the ejected electron from the ionized atom is 3.6 × 10⁵ m/s