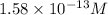Answer : The final hydrogen ion concentration is
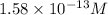
Explanation :
The chemical reaction equation will be:
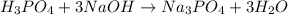
In this reaction, 1 mole of
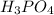 reacts with 3 mole NaOH.
reacts with 3 mole NaOH.
So, the number of moles of
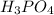 present in 150 ml of 0.1 M solution is calculated as follows.
present in 150 ml of 0.1 M solution is calculated as follows.
Number of moles = Concentration × Volume
Number of moles = 0.1 M ×0.150 L = 0.015 mol
As it reacts with 3 moles of NaOH.
Number of moles of NaOH = 3 × 0.015 mol = 0.045 mol
So, moles of NaOH in 400 mL of 0.2 M NaOH is as follows.
Number of moles = 0.2 M × 0.4 L = 0.080 mol
Number of moles remained after the reaction = (0.080 - 0.045) mol = 0.035 mol NaOH in 550 ml (400 ml + 150 ml)
As molarity is the number of moles present in liter of solution. Hence, molarity of NaOH is as follows.
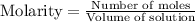
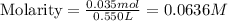
Now we have to determine the hydroxide ion concentration.
As,
![[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hmlln255qbj8yqsk7ge707ryw787o8ibi2.png) = 0.0636 M
= 0.0636 M
![pOH=-\log [OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hdm1ob4dj6mx2sy3kobrrj91lzbh3927bk.png)
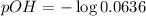
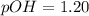
Now we have to determine the pH.
As, pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 - pOH
pH = 14 - 1.20
pH = 12.8
Now we have to determine the hydrogen ion concentration.
![pH=-\log [H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/rjo2yhb5oj9ry1fr4db1ujrazm6fh3vhke.png)
![12.8=-\log [H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nxx5nqx7yro4tbye1icxyzmm1kygh6o2o3.png)
![[H^+]=1.58* 10^(-13)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/o4b2ivexhkacpkunazcsr7y7m77gt2r71a.png)
Therefore, the final hydrogen ion concentration is