Answer:
a)
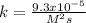
b)
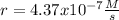
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, given that the reaction is second order in NO and first order in O2, the rate law is written as follows:
![r=k[NO]^2[O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ta2xhx6ya9htfjjo2ph0n386rhbkqu1iua.png)
In such a way, for a rate law of 0.00022022 M/s and the concentrations of NO and O2 0.8M and 3.7M respectively, the rate constant is:
![k=(r)/([NO]^2[O_2])\\\\k=(0.00022022M/s)/((0.8M)^2(3.7M)) \\\\k=(9.3x10^(-5))/(M^2s)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/9ujki4rm72ynezjd5qdx4bwnjbz5q20qgx.png)
Thus, for the new concentrations of NO and O2 0.1M and 0.47M respectively, the rate is:
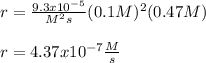
Regards.