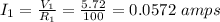Answer:
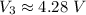
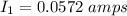
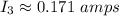
Step-by-step explanation:
Notice that this is a circuit with resistors R1 and R2 in parallel, connected to resistor R3 in series. It is what is called a parallel-series combination.
So we first find the equivalent resistance for the two resistors in parallel:
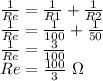
By knowing this, we can estimate the total current through the circuit,:
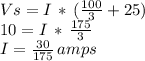
So approximately 0.17 amps
and therefore, we can estimate the voltage drop (V3) in R3 uisng Ohm's law:
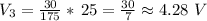
So now we know that the potential drop across the parellel resistors must be:
10 V - 4.28 V = 5.72 V
and with this info, we can calculate the current through R1 using Ohm's Law: