Answer:
G = 6.6675 x
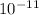 N
N
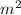 /
/
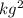
Step-by-step explanation:
From Newton's law of universal gravitation,
F =
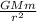 .................. 1
.................. 1
Where F is the force of attraction, G is the universal gravitation constant, M is the mass of a massive object e.g earth, m is the mass of the smaller object e.g moon, r is the radius of the massive object.
Newton's second law states;
F = mg ................... 2
F is the force, m is the mass of the object and g is the gravitational force on the object.
Equating equations 1 and 2 gives;
mg =
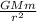
So that;
g =
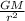
⇒ G =
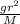
where: g = 9.81 m/
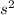 , r = 6371 km, M = 5.972 x
, r = 6371 km, M = 5.972 x
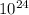 kg.
kg.
G =
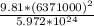
=
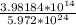
= 6.6675 x
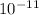 N
N
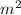 /
/
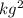
The Universal Gravitational Constant (G) is 6.6675 x
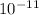 N
N
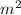 /
/
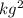 .
.