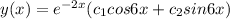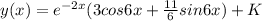Answer:
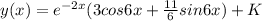
Explanation:
Given the initial value problem y′′+4y′+40y=0 where y(0)= 3 and y′(0)=5.
Find the solution in the attached file.
Since the solution is a complex number, the solution to the second order differential equation is given as shown;
y(x) =
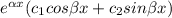
from the complex solution D = -2+6i
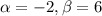
y(x) =
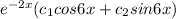
Substituting the initial values
when y(0) = 3, the solution becomes;
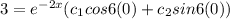
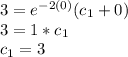
From y(x) =
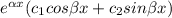
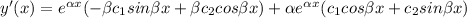
at y'(0) = 5, the solution becomes;
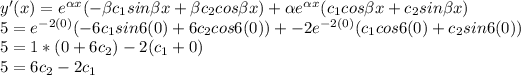
Since c₁ = 3;
5 = 6c₂ - 2(3)
5 = 6c₂ - 6
6c₂ = 11
c₂ = 11/6
Substituting the constant into the solution to the differential equation