Answer:
The equilibrium constant for CO now
= 0.212 M
For H₂O
= 0.212 M
For CO₂ = x = 0.2880 M
For H₂ = x = 0.2880 M
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the reaction is:
CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g)
The ICE Table for this reaction can be represented as follows:
CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g)
Initial 0.5 0.5 - -
Change -x -x + x + x
Equilibrium 0.5 -x 0.5 - x
The equilibrium constant
![K_c = ([x][x])/([0.5-x][0.5-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/p9gqxggh6jvam4256f9hg3riu8hocs62zt.png)
![K_c = ([x]^2)/([0.5-x]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7t8la0fkf4yymj7r0bkmom15v87ay4h93e.png)
where;

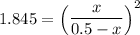
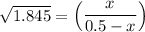
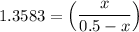
1.3583 (0.5-x) = x
0.67915 - 1.3583x = x
0.67915 = x + 1.3583x
0.67915 = 2.3583x
x = 0.67915/2.3583
x = 0.2880
The equilibrium constant for CO now = 0.5 - x
= 0.5 - 0.2880
= 0.212 M
For H₂O = 0.5 - x
= 0.5 - 0.2880
= 0.212 M
For CO₂ = x = 0.2880 M
For H₂ = x = 0.2880 M