Answer:
The pH of the solution is 4.69
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Mass of potassium = 2.643 grams
Weight of water = 50.00 mL
Weight of HCl=100.00 ml
Mole = 0.120 M
We know that,
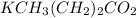 is a basic salt.
is a basic salt.
Let's write it as KY.
The acid
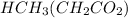 would become HY.
would become HY.
We need to calculate the moles of KY
Using formula of moles
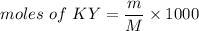
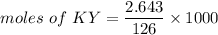
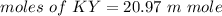
The reaction is
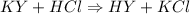
The number of moles of KY is 20.98 m
initial moles = 20.98
Final moles
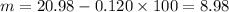
We need to calculate the value of pKa(HY)
Using formula for pKa(HY)
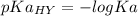
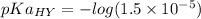
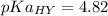
We need to calculate the pH of the solution
Using formula of pH
![pH=pKa+log(([KY])/([KH]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/pdtowyp8dn5f0egqzfib8sq7cw7tfy7bpj.png)
Put the value into the formula
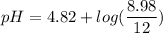
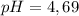
Hence, The pH of the solution is 4.69