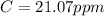Answer:
The value is
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The volume of the first aliquot is
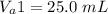
The volume after dilution is
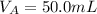
The Absorbance of the first solution is
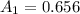
The wavelength at which the absorbance occurred is
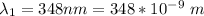
The length of the cell
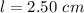
The volume the second aliquot is
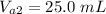
The volume of the solution it was mixed with is
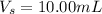
The concentration of quinine in the 10 mL solution
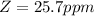
The volume of the second solution after dilution is
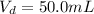
The absorbance of the second solution is
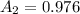
Generally the concentration of quinine is mathematically represented as
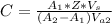
=>
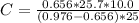
=>