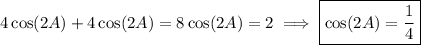Use the angle sum identities to expand
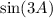 and
and
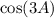 :
:
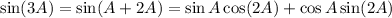
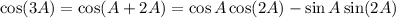
Use the double angle identity to expand
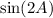 :
:
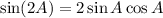
So we have
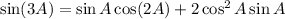
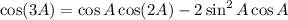
Then divide the first expression by
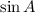 and the second by
and the second by
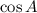 :
:
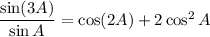
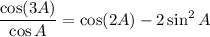
Squaring these gives
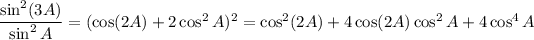
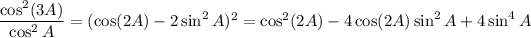
Subtract the second expression from the first to get the original equation. The
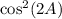 terms cancel, leaving us with
terms cancel, leaving us with
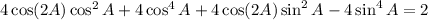
Now, notice that
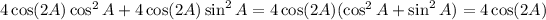
and
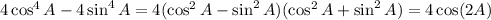
because
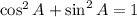 and
and
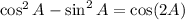 .
.
So we're left with