Answer: Choice (a) in the upper left corner
Angle A = 68 degrees
Angle B = 22 degrees
Side AB = 2.9 cm
The three values are approximate
=========================================================
Step-by-step explanation:
a = BC = 2.7 and b = AC = 1.1 are the two legs of the right triangle.
Use the pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
2.7^2 + 1.1^2 = c^2
8.5 = c^2
c^2 = 8.5
c = sqrt(8.5)
c = 2.91547594742266
c = 2.9
The hypotenuse is c = AB = 2.9
--------------------
We then use trig ratios to find the two missing angles.
Let's say we ignore the hypotenuse and focus on the two legs of the triangle.
With respect to reference angle A, side BC is opposite and AC is adjacent
Use the tangent ratio to get
tan(angle) = opposite/adjacent
tan(A) = BC/AC
tan(A) = 2.7/1.1
tan(A) = 2.45454545454546
A = arctan(2.45454545454546)
A = 67.8336541779176
A = 68
Note: arctan is the same as inverse tangent or
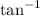 . Make sure your calculator is in degree mode.
. Make sure your calculator is in degree mode.
-------------------
Similarly,
tan(angle) = opposite/adjacent
tan(B) = AC/BC
tan(B) = 1.1/2.7
tan(B) = 0.4074074074074
B = arctan(0.4074074074074)
B = 22.166345822082
B = 22
Or you could use the value of A to get B = 90-A = 90-68 = 22. This works because A+B = 90 as we're working with a right triangle. In other words, A and B are complementary angles.
-------------------
In summary we found
A = 68
B = 22
AB = 2.9