Answer:
-27.2 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
We can use the heat-transfer formula. Recall that:
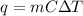
Where m is the mass, C is the substance's specific heat, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Hence substitute:
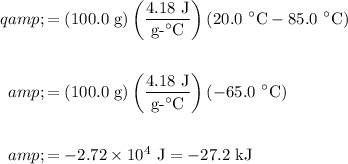
Therefore, the cooling of the water released about 27.2 kJ of heat.